Parasite, Bacteria and Virus Population Increase
Temperature, precipitation, humidity, and other climatic factors affect the reproduction, development, behavior, and population dynamics of viruses, bacteria, and parasites. Insect vectors have several physical traits that help them take advantage of climate impacts like flooding, increased precipitation, and warmer weather.
Read MoreDec 16, 2019 | Princeton University
Climate change could make RSV respiratory infection outbreaks less severe, more common
Nov 12, 2019 | CNN
There's a hidden consequence of climate change: A deadly virus that's killing key marine species

Aug 28, 2019 | Reuters
As the climate shifts, Central America confronts a deadly dengue...

Aug 21, 2017 | Naval Research Laboratory
Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia Watch
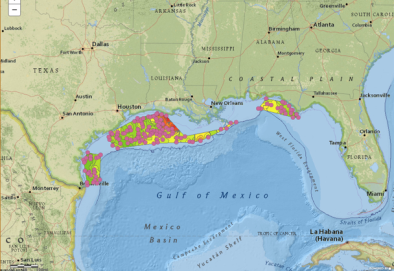
Jan 24, 2017 | Boston Children's Hospital
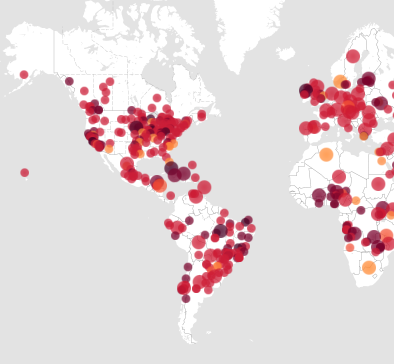
Global Health Map
Mar 29, 2016 | Tick Encounter Resource Center, University of Rhode Island
Current US Tick Activity
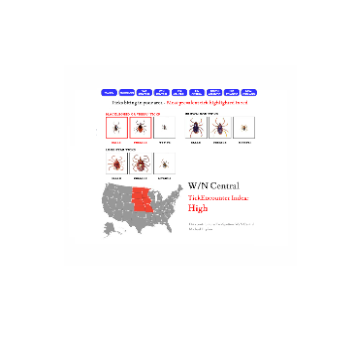
Nov 12, 2019 | Scientific Reports
Viral emergence in marine mammals in the North Pacific may be linked to Arctic sea ice reduction
Jul 27, 2017 | Scientific Reports
Surges in trematode prevalence linked to centennial-scale flooding events in the Adriatic
Apr 4, 2017 | MMWR. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report
Vital Signs: Update on Zika Virus–Associated Birth Defects and Evaluation of All U.S. Infants with Congenital Zika Virus Exposure — U.S. Zika Pregnancy Registry, 2016
Earth Systems Signals
Global warming is causing widespread and rapid changes in the atmosphere, ocean, cryosphere and biosphere.
Heat Signals
The Earth is getting hotter due to human activities that release heat-trapping gases into the atmosphere.
Drought Signals
Climate change is making droughts more likely to occur, and more severe when they do.
Wildfires Signals
Climate change is increasing the size, frequency, intensity and seasonality of wildfires.
Hurricanes Signals
Warmer temperatures increase the rate of water evaporation, which feeds moisture and energy into storms.
Floods Signals
Worsening floods due to climate change are putting a growing number of communities at risk.