Bigger, stronger, rainier: Is Hawaii’s Hurricane Lane a sign of what’s to come?

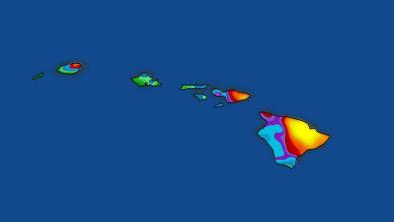
Hurricane Lane, one of the strongest hurricanes ever measured in the Central Pacific Ocean, is on a crash course with paradise.
At the peak of its intensity late Tuesday and early Wednesday, Lane had sustained winds of 160 mph and gusts up to nearly 200 mph — making it the most powerful hurricane to threaten Hawaii on record. The storm, now downgraded from Category 5 to 4, poses a colossal threat to the islands: The National Weather Service says that “life-threatening impacts are likely.”
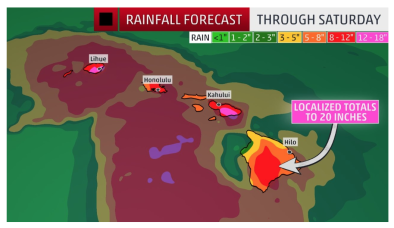
On Lane’s current track, Hawaii could see torrential downpours, mudslides, and 20-foot waves. The desert-like parts of the tropical islands could witness a year’s worth of rain, up to 2 feet, in mere hours. Lane should weaken as it approaches, but it could still bring tropical-storm-force winds to almost every part of every island — winds strong enough to tear roofs off homes and cause widespread power outages that could last weeks or months.
...
As the waters of the Central Pacific warm, hurricanes like Lane are expected to become more common — and indeed, the Pacific has seen a flurry of hurricanes near Hawaii in recent years. While the hurricane threat to Hawaii tends to peak during El Niño years, recent research shows that long-term ocean warming, not El Niño, is likely the dominant cause of Hawaii’s growing hurricane threat. And Hawaiian scientists have found these new hurricanes tend to be larger, stronger, and rainier.
...
In addition to sea-level rise and coral bleaching, hurricanes are increasingly part of Hawaii’s reality. For his part, the governor is putting Hawaii on a path to reduce its contribution to climate change. In 2015, Ige signed legislation making the state the first in the nation to mandate 100 percent renewable energy — a goal it plans to reach by 2045.
Related Content