Science Source
Perception of climate change
- States that “climate dice,” describing the chance of unusually warm or cool seasons, have become more and more “loaded” in the past 30 y, coincident with rapid global warming
- Finds the distribution of seasonal mean temperature anomalies has shifted toward higher temperatures and the range of anomalies has increased
- Finds an important change is the emergence of a category of summertime extremely hot outliers, more than three standard deviations (3σ) warmer than the climatology of the 1951–1980 base period
- Holds that this hot extreme, which covered much less than 1% of Earth’s surface during the base period, now typically covers about 10% of the land area
- Says it follows that we can state, with a high degree of confidence, that extreme anomalies such as those in Texas and Oklahoma in 2011 and Moscow in 2010 were a consequence of global warming because their likelihood in the absence of global warming was exceedingly small
- Discusses the practical implications of this substantial, growing, climate change
Related Content
Headline
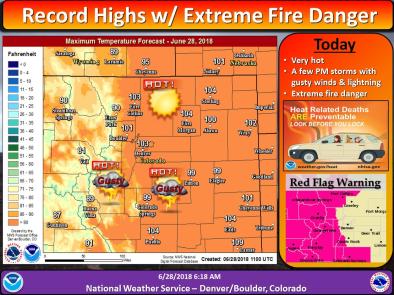
Jun 29, 2018 | The Denver Post
Denver’s scorching hot weather on Thursday tied an all-time record, a roasting 105
Headline

Jun 28, 2018 | Business Insider
A major heat wave is about to fry the East Coast — here's what's coming
Headline
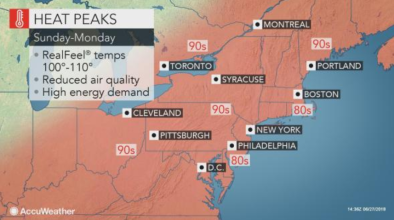
Jun 28, 2018 | AccuWeather
Most intense heat to peak ahead of July 4th in northeastern US
Headline

Jun 28, 2018 | USA Today
Dangerous, oppressive heat wave to scorch central, eastern US as 'heat dome' expands


