Science Source
The Impact of Climate Change and Variability on Heavy Precipitation, Floods, and Droughts
- States there is a direct influence of global warming on changes in precipitation and heavy rains
- States that increased heating leads to greater evaporation and thus surface drying, thereby increasing intensity and duration of drought
- States that, in contrast to surface drying, the water-holding capacity of air increases by about 7% per 1 °C warming, which leads to increased water vapor in the atmosphere
- Holds increased atmospheric moisture probably provides the biggest influence on precipitation—storms, whether individual thunderstorms, extratropical rain or snow storms, or tropical cyclones and hurricanes, supplied by increased moisture, produce more intense precipitation events that are widely observed to be occurring, even in places where total precipitation is decreasing
- Says more intense precipitation events increases the risk of flooding
- Finds that patterns of where it rains also have been observed to change, with dry areas becoming drier (generally throughout the subtropics) and wet areas becoming wetter, especially in mid to high latitudes
- Finds that this pattern is simulated by climate models and is projected to continue into the future
- Finds that, since more precipitation occurs as rain instead of snow with warming, and snow melts earlier, there is increased runoff and risk of flooding in early spring, but increased risk of drought in deep summer, especially over continental areas
Related Content
Headline
Aug 10, 2016 | Weather Underground
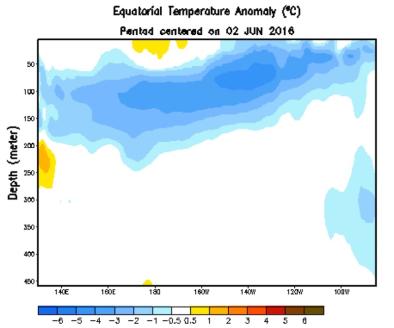
El Niño is Officially Over—and La Niña is Likely On the Way
Headline

Aug 10, 2016 | Phys.org
Sierra Nevada snowpack not likely to recover from drought until 2019
Headline
Aug 10, 2016 | The Weather Channel
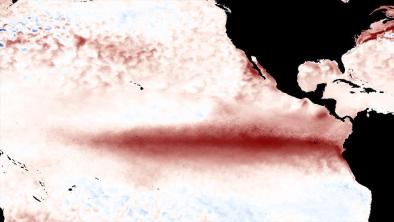
Current El Niño Ties 1997-1998 as Strongest on Record, Says NOAA
Science Source
| Geophysical Research Letters
Characterizing the extreme 2015 snowpack deficit in the Sierra Nevada (USA) and the implications for drought recovery
Margulis, Steven A., Cortés et al


