Science Source
Detecting anthropogenic footprints in sea level rise
- Provides a probabilistic upper range of long-term persistent natural GMSL/LMSL variability (P=0.99), which in turn, determines the minimum/maximum anthropogenic contribution to sea level rise since 1900
- Concludes that it is virtually certain (P=0.99) that at least 45% of the observed increase in GMSL is of anthropogenic origin
Related Content
Real Time Data
Oct 6, 2016 | NOAA Tides and Currents
US Daily Coastal Water Levels
Science Source
| NOAA and NCEI
2015 State of U.S. “Nuisance” Tidal Flooding
William V. Sweet, John J. Marra
Science Source
| NOAA Technical Report
Sea Level Rise and Nuisance Flood Frequency Changes around the United States
William Sweet, Joseph Park, John Marra et al
Real Time Data
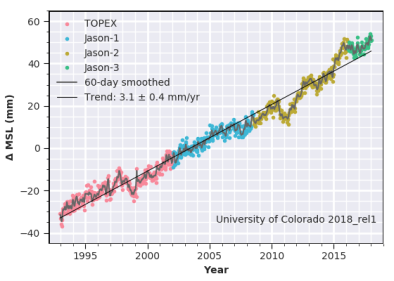
Feb 25, 2016 | University of Colorado Sea Level Research Group
Global Mean Sea Level Time Series


