Science Source
Assessing the climate‐scale variability of atmospheric rivers affecting western North America
- Creates a new seven‐decade‐long catalog of atmospheric river behavior land‐falling upon the west coast of North America
- States that the catalog has been validated against independent precipitation observations to ensure that the atmospheric rivers represented therein are associated with extreme orographic precipitation
- The results clearly delineate a prominent role for atmospheric rivers in California's hydroclimate
- States that atmospheric river variability has been particularly important in the recent California drought as well as its most recent lapse
- Detects a long‐term increasing trend in water vapor transport impinging on the west coast of North America associated with atmospheric rivers and overall wintertime water vapor transport associated with climate warming
- The results, moreover, suggest that potential predictability of seasonal behavior of atmospheric rivers may hinge on sources of climatic variability somewhat different from that of total water vapor transport
Related Content
Headline

Feb 14, 2019 | The Weather Channel
California Rain Triggers Evacuations, Mudslides; Woman Rescued from Sausalito Home
Headline

Feb 14, 2019 | Reuters
Mudslide risk from California storm forces hundreds to evacuate
Headline

Feb 13, 2019 | San Francisco Chronicle
Heavy storms shuts down SFO flights, floods roadways across region
Headline
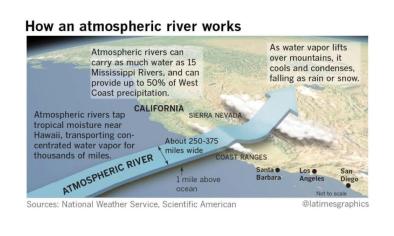
Feb 13, 2019 | LA Times
As atmospheric rivers pound California, here comes the season’s ‘biggest storm’


