Science Source
Attributing the US Southwest's recent shift into drier conditions
- States that the US Southwest has been getting drier and warmer over the last few decades
- States that these changes fit the common narrative of what might be expected to happen in response to increasing greenhouse gas concentrations
- States that natural variability of precipitation and temperature is known to be large in this region, making it difficult to clearly attribute the recent drying and warming to greenhouse gas forcing
- Shows that while the warming is largely due to greenhouse gas forcing, the drying is mostly due to internal climate variability
- Finds that only an insignificant drying remains after accounting for this internal climate variability
- Notes that unlike previous studies that relied exclusively on climate models, this study bases its conclusions on a combination of observations, an empirical statistical method, and climate models
Related Content
Science Source
| Scientific Reports
Influence of Anthropogenic Climate Change on Planetary Wave Resonance and Extreme Weather Events
Michael E. Mann, Stefan Rahmstorf, Kai Kornhuber et al
Real Time Data
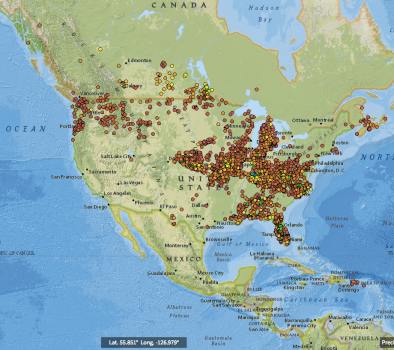
Jul 15, 2016 | NOAA / NCDC
US Daily Temperature and Precipitation Summaries
Science Source
| National Weather Service and Penn State University Monograph
Recent Trends in Northern and Southern Hemispheric Cold and Warm Pockets
Richard Grumm and Anne Balogh
Real Time Data
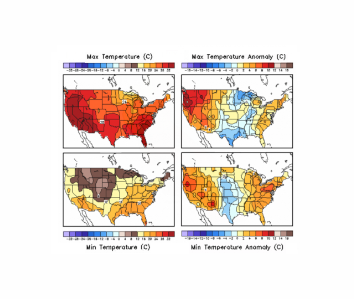
Jun 6, 2016 | Climate Prediction Center | NOAA
US Daily Temperature Analyses


