Climate Change Contributed to Oroville Spillway Collapse, Study Says

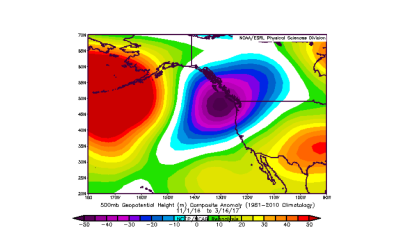
A new study suggests global warming and its impacts on the Sierra Nevada's snowpack and runoff contributed to the collapse of central California's Oroville Dam spillway in February 2017.
The study published this month in the Journal of Geophysical Research Letters investigated temperature impacts on snowpack and runoff‐driven flood risk in the Sierra Nevada during the extremely wet year of 2016–2017.
The team of researchers from the University of California Los Angeles determined that warming that year increased the Sierra Nevada's early‐season snowpack runoff by 30 percent.
"In the Feather River Watershed, historical warming increased runoff by over one third during the period of heaviest precipitation in February 2017," the authors wrote. "This suggests that historical anthropogenic warming may have exacerbated runoff conditions underlying the Oroville Dam spillway overflow that occurred."
Related Content